The Museum of Neoliberalism
I was saddened to learn that The Museum of Neoliberalism is closing (see here). It is located near Lewisham and I visited in November 2023.
In this article I wanted to share 5 points that came to mind as I looked around.
(1) There is a tendency for critics of neoliberalism to present a conspiracy theory view of the movement. The museum presents this in the following way:

I mean, they even used red thread!

The serious point is that these outside accounts don’t match my inside knowledge, and I don’t believe that’s due to naivety on my part. I’m a senior fellow of the Adam Smith Institute and disagree that they constitute a “total perversion of Smith’s ideas”, but welcome an intellectual conversation about that claim. Back in 2016 Sam Bowman (then Executive Director at the ASI) wrote an article called “I’m a neoliberal. Maybe you are too” and yet I’ve not seen an honest engagement with them.
Ultimately, I think that the truth is less exciting than the museum depicts – these think tanks are transparent with their objectives and activities, punch above their weight in terms of resources, but have little direct power or influence. It’s an error to present them as something they are not.
(2) There is lots to be said about what has happened to economic inequality (and why) over the course of the twentieth century (my teaching materials are here). But the idea that governments responded to falling inequality by increasing prices is simply wrong. Milton Friedman’s monetarist prescriptions were a response to the prevalent inflation, and succeeded in controlling it. That inflation was a result of excessive money creation, in part due to the fiscal profligacy of government spending. The chronology is clear – neoliberalism gained dominance within the context of high inflation, and sought to combat it. It did not generate inflation as a means to reverse declining inequality.

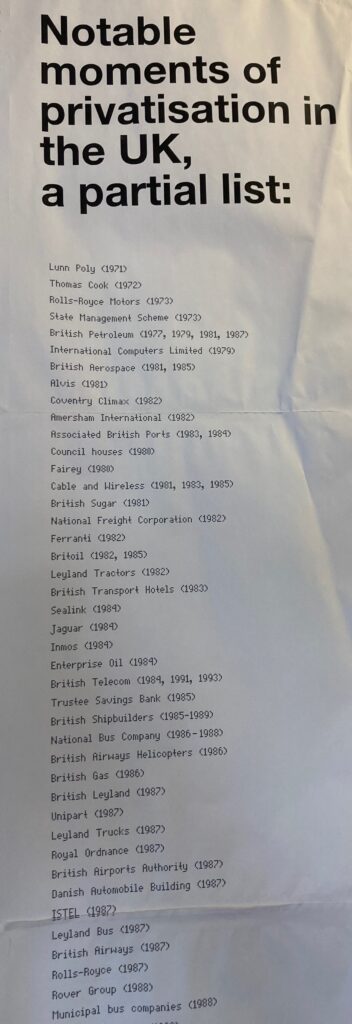
(3) There is this a long list of notable moments of privatisation in the UK. I suspect the assumption is that because people typically don’t like privatisation, this is persuasive. However, the paradox of privatization is that although most people believe that the process by which assets are returned to private ownership is often flawed, they typically do not want the state to control those industries. (Note that the solution, therefore, is to avoid nationalisation in the first place.)
But when you actually look at these companies – Lunn Poly, Thomas Cook – does anyone really want state ownership of travel agents? Is Rolls Royce really a company that the UK government has to manage and run? Really?
(4) The section on “bullshit jobs” exposes poor working practices and elicits sympathy for workers who lack certain employment rights. In my view, though, the last thing you should do in such situations is to take away options. And yet this is what higher labour standards, by imposing costs on employers, tend to do. Ultimately I find these sorts of judgments elitist and snobbish. There’s a million jobs I’d hate to do, but any job that someone voluntarily agrees to, because they view it as an improvement over their next best alternative, is ok by me. Generally speaking, the gig economy has been a liberation within the context of excessive restrictions on labour.

(5) And what’s the conclusion? Well this final panel, called “there is an alternative” sums things up nicely. Apparently
“the current crisis is an open moment of possibility in which the world will step beyond it into something else. What that ‘something else’ looks like is up to you.”

Forgive me, but I do not see an articulation of an alternative. This does nothing to dispense the fear that the alternative to a free market system of private property rights is a utopian nonsense.
I love the concept of a Museum of Neoliberalism and am sorry that it is closing. I found it provocative and hope you enjoyed my reflections.